blog
22 June 2022
There’s no escaping the fact that the way businesses consume IT resources is rapidly changing. Cloud computing is increasingly popular and has brought a fundamental shift away from the traditional investments in on-premises IT infrastructure and skilled people to support it. Instead, Cloud offers an ‘as-a-Service’ model, whereby IT infrastructure and applications can be simply acquired and provisioned over the internet. This gives businesses unprecedented opportunity to scale and transform, without the limitations of their IT infrastructure standing in the way.
Cloud brings new terminology to be familiar with and when deciding whether they’re right for you, it is important to the condenser which elements you would like to manage and which you would like to provide for you as a service:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
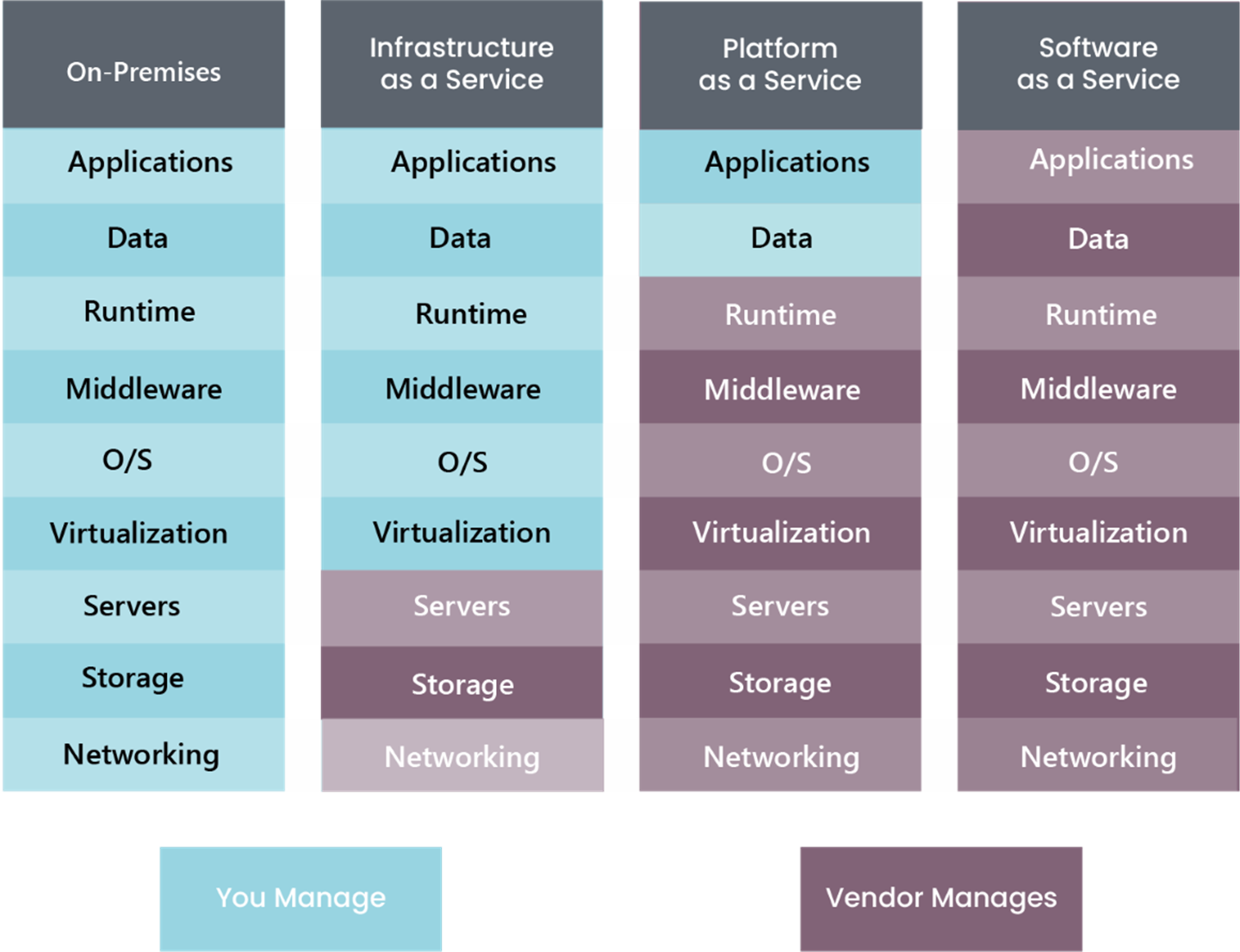
In this blog, we’ll explain what each means and the benefits and risks that come with them, but firstly;
Why cloud is so important to understand
The simple answer is ‘growth and transformation’.
The pandemic meant that businesses needed to suddenly change how they operate on a global scale – workforces suddenly became remote wherever possible and e-commerce became a new norm. Cloud made this transformation possible and now that leap has been made, it brings a new agility and competitive edge to businesses that even late adopters of the cloud now need to keep pace with. Those that don’t keep up, risk becoming obsolete or relegated to low-growth markets, as stated in a 2022 report from Gartner that indicated that cloud spending would reach $1.8trillion by 2025.
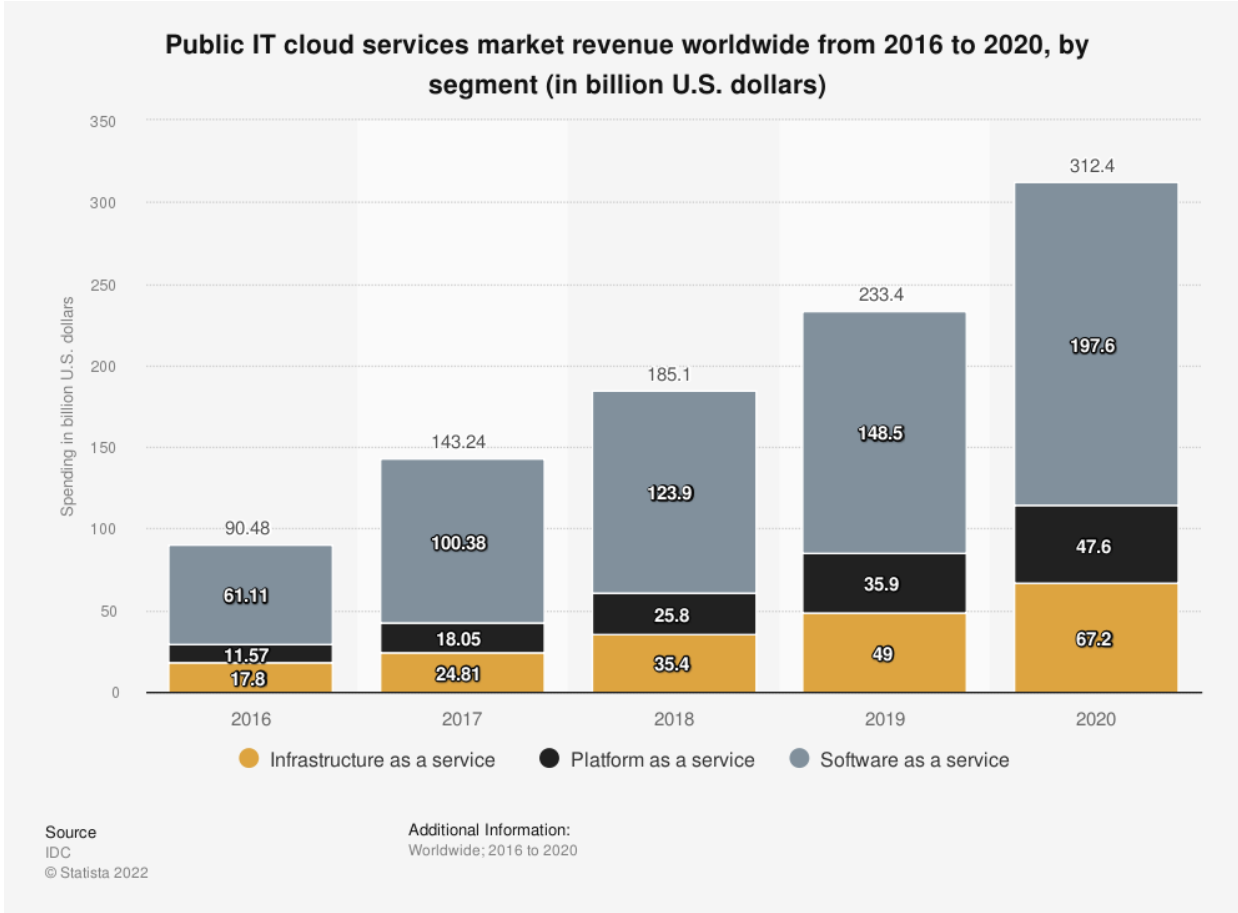
2025 also presents the tipping point, whereby investment in technologies that can be delivered by cloud models will overtake on-premises investment for the first time.
The benefits and risks of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS, often referred to as simply cloud infrastructure services, replaces the need to invest, install, support and maintain traditional storage and computing hardware. Common uses of IaaS include Start ups, Disaster Recovery, Ecommerce, Internet of Things (IOT), AI, and Software Development.
Examples: Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
IaaS Benefits
- Highly scalable – additional resources can be easily provisioned.
- Flexible – pay for the resources you need, as you need it
- High-performance.
- Accessible by multiple users.
- Can be cost-effective compared to on-premises hardware investments.
- Security – the cloud is generally very secure and makes DR and backup processes easier.
- Maintain Control – infrastructure is maintained for you but you have control over what you do with it – unlike with an outsourcer.
IaaS Concerns
- Compatibility – you may have legacy systems that are not compatible with cloud-based services and may require upgrading or replacing.
- Overspending – cloud resources come at a premium, so need strong governance processes, including diligent cloud tagging to avoid wasted spend on resources that aren’t delivering business value.
- Cost management – can become complex if accountability for resources is devolved out to business units and stakeholders who drive the demand. Adopting FinOps practices can help to create a new operating model with greater communication to manage the cloud.
- Skills – there is a Cloud skills gap across the industry, it may be worthwhile investing in training to overcome it and make sure you can maintain control.
- Management can become complex, especially if you have a multi-cloud environment spanning different cloud vendors. A multi-cloud management solution will enable you to see and centralize reporting for accuracy on your costs and utilization.
- Shadow IT – the term used to describe when cloud resources are managed outside the control of IT, leading to a risk of unmanaged spending and data security. Again, a Cloud Asset Management solution will ensure everything remains visible.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Examples: Google App Engine AWS Elastic Beanstalk Windows Azure Heroku Force.com. OpenShift
PaaS typically describes a framework whereby developers can create and customize applications from the cloud without having the traditional on-premises overhead of providing and maintaining the server infrastructure, programming software and security protocols to do so. This means that developers still have control over the applications, but without the burden of running the additional infrastructure.
Typical uses for PaaS include API development and management, DevOps and agile development, Internet of Things (IOT), containers, Kubernetes and serverless computing.
PaaS Benefits
- Applications developed on PaaS often adopt the hyper-scalable and available characteristics of the cloud.
- Faster development, with easier collaboration.
- Development infrastructure often needs to flex, so with PaaS you can expand and reduce resources as required and only simply Pay-as-you-go.
- High availability and scalability.
- Coding is decreased and dev teams don’t have to worry about things like load balancing and OS patching.
PaaS Concerns
- Legacy integrations – custom software applications developed internally often need to integrate with other legacy systems across the business. If legacy systems aren’t compatible with PaaS, new apps may not be able to be developed using PaaS.
- PaaS solutions may limit control capability for end users, as it’s designed to reduce the operational overhead. In some instances, this may become prohibitive.
- Some framework versions may not perform well with PaaS services, impacting runtime.
- Vendor lock-in – if the PaaS vendor does not provide adequate migration policies, you may become locked-in to one platform.
- Security options may become restricted by compatibility issues with the PaaS platform.
- Cost-management – diligence is required to ensure that instances are properly managed and decommissioned after use or right-sized if not done automatically.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS or ‘cloud application services’ is the full removal of all provisioning and operating overheads from an application, meaning that all you need to do as a user is sign in through a web browser and have an active subscription to the solution. Simply pay a monthly of the annual fee. By far the most favoured option for applications to be delivered now, SaaS opens up the availability of business applications to users regardless of location and increasingly without requiring any download to users’ devices.
Typical uses include Email, Social Media, communications, data storage, customer relationship management (CRM), workflow management, and creative apps.
Examples: Microsoft365 Google Workspace Salesforce.com Adobe Creative Cloud Dropbox Trello
SaaS Benefits
- Highly accessible – simply log in through a web browser from anywhere.
- Typically, no installations are required on clients, so provisioning apps to staff just requires an internet connection and subscription activation.
- Software is always upgraded and in support.
- Security patches are applied automictically.
- Zero overhead relating to maintenance, support, upgrades, infrastructure support, middleware, storage and server software licensing to host applications.
- Assured application availability, performance and security under an SLA.
- Flexible – additional functionality can typically be added on to licence types.
- No software licence compliance risk, though SaaS cost management is still critical.
SaaS Concerns
- Some apps are not as fully-featured as their on-premises counterparts and users may take some time to adjust if familiar with legacy versions e.g. office apps.
- Cost management can spiral out of control unless diligent processes are in place to ensure that you don’t have redundant subscriptions costing money and delivering no business value – starters and leavers processes need to feed in to decommissioning processes for SaaS applications. Typically, 30% of SaaS spend is wasted. SaaS Management solutions can illuminate precisely where wastage is occurring for simpler management and cost savings (see this case study about a $1.6m saving with O365)
- Less Control – whilst the benefits of SaaS mean that you’re always patched and up-to-date on the latest version, it also means that favoured versions can’t be kept any longer than the vendor wants you to. As a disadvantage, this is largely eclipsed by the fact that you don’t need to upgrade user devices to move to a newer version, decreasing end-user hardware costs.
- Data Security – your business information is out of your hands, so make sure you’re confident in the SaaS vendors you’re using and be sure to deactivate subscriptions belonging to ex-employees
Summary
There are plenty of benefits to ‘as-a-service’ models and as businesses recover from the urgency of the pandemic, now is the time to stop and assess where they are with the cloud and to make sure that the right governance and controls are in place to maximize those benefits moving forward.
There are two sides to ‘cloud management’ – the technical and strategic assessment/migration of services to the cloud and the ongoing commercial management of cloud costs, performance and optimization.
The market offers tooling and services to help, but so far solutions have been focused on the ‘operational’ side migration to the cloud. As cloud maturity increases and businesses become aware of the growing need to optimize cloud costs that can easily spiral out of control, ‘cloud asset management’ solutions are needed to give organisations the unified, holistic visibility and control over multi-cloud and the ability to streamline cost management, FinOps and optimization processes.
For help understanding your cloud world, contact Vitado today.
Related Articles
7 Challenges of Managing the Cloud
Managing cloud resources as business assets is still relatively new for many. That is – managing these resources not just in terms of provisioning or migrating workloads to them, but controlling cloud costs to the business with meaning. These costs need to be understood, justified and controlled with unprecedented accountability across business functions, representing the business need for which these new premium resources are consumed.
What To Consider When Moving to the Cloud
Managing cloud resources as business assets is still relatively new for many. That is – managing these resources not just in terms of provisioning or migrating workloads to them, but controlling cloud costs to the business with meaning. These costs need to be understood, justified and controlled with unprecedented accountability across business functions, representing the business need for which these new premium resources are consumed.
Public, Private & Hybrid Cloud Explained
Managing cloud resources as business assets is still relatively new for many. That is – managing these resources not just in terms of provisioning or migrating workloads to them, but controlling cloud costs to the business with meaning. These costs need to be understood, justified and controlled with unprecedented accountability across business functions, representing the business need for which these new premium resources are consumed.
How Vitado can help
Vitado offer helpful cloud management services and a unified technology platform to provide the full visibility and proactive alerting to gaps in processes and standards that helps to streamline cloud management and active cloud cost-optimization. To find out more about the Vitado solution, to arrange a demo or to speak to your local Vitado team about any of our services, simply contact us today.
Find out more:
Vitado Guide to FinOps Blog#2: How to Gain Sponsorship and Implement a New Structure
Complete Guide to Cloud Tagging– Download the e-book
Contact Vitado – Vitado has a global team of experts in managing IT costs, so if you want to begin solving your technology challenges, our unique technology and services are here to help.
Stay Up to Date With The Latest News & Updates
Get Control
Its time to take control of your Cloud estate. Vitado can help you gain visibility, ensure governance, control and manage costs.
Follow Us
Want to keep up to date with the latest in cloud? Check out our social media profiles
